Automated Benign V/S Malignant Nodule in Chest X-ray
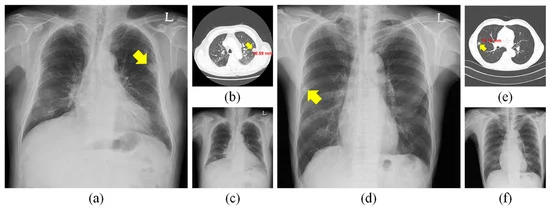
Automated benign vs. malignant nodule detection in chest X-rays using artificial intelligence (AI) is a cutting-edge application in medical imaging that holds significant promise for early detection and diagnosis of lung cancer. Here’s how it works and its key aspects:
- Image Analysis: AI algorithms analyze chest X-ray images to identify and classify pulmonary nodules as benign or malignant based on their size, shape, density, margins, and other imaging features. These algorithms are trained on large datasets of annotated chest X-rays to learn patterns associated with different types of nodules.
- Feature Extraction: AI algorithms extract quantitative features from chest X-ray images, such as nodule size, shape irregularity, spiculation, calcification, and surrounding tissue characteristics. These features are used to develop predictive models that differentiate between benign and malignant nodules with high accuracy.
- Machine Learning Techniques: Machine learning techniques, including deep learning, convolutional neural networks (CNNs), and ensemble methods, are commonly used to train AI algorithms for nodule classification. These techniques enable the algorithms to automatically learn complex patterns and relationships in chest X-ray images, leading to more accurate and reliable predictions.
- Validation and Evaluation: Automated benign vs. malignant nodule detection systems undergo rigorous validation and evaluation to assess their performance and generalizability. This involves testing the algorithms on independent datasets, comparing their predictions with ground truth annotations provided by expert radiologists, and measuring metrics such as sensitivity, specificity, accuracy, and area under the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve.
- Clinical Integration: Automated nodule detection systems are integrated into radiology workflow to assist radiologists in interpreting chest X-rays and detecting suspicious nodules. These systems provide real-time feedback and decision support, helping radiologists prioritize cases for further evaluation and expedite patient management.
- Risk Stratification and Patient Management: AI-powered nodule detection systems enable risk stratification and personalized patient management strategies based on the likelihood of malignancy. Patients with high-risk nodules may undergo additional imaging studies (e.g., CT scans), biopsy procedures, or referral to lung cancer specialists for further evaluation and treatment planning.
- Continuous Improvement: Automated nodule detection systems continuously learn and improve over time through feedback mechanisms and updates based on new data and research findings. As more chest X-ray images become available for analysis and as algorithms are refined and optimized, the performance and accuracy of automated nodule detection systems are expected to further improve.
In summary, automated benign vs. malignant nodule detection in chest X-rays using AI represents a promising advancement in lung cancer screening and diagnosis. By leveraging the power of artificial intelligence and machine learning, these systems have the potential to improve early detection rates, reduce diagnostic errors, and ultimately save lives by facilitating timely intervention and treatment for patients with lung cancer.
