Audit Work for X-Ray Reporting
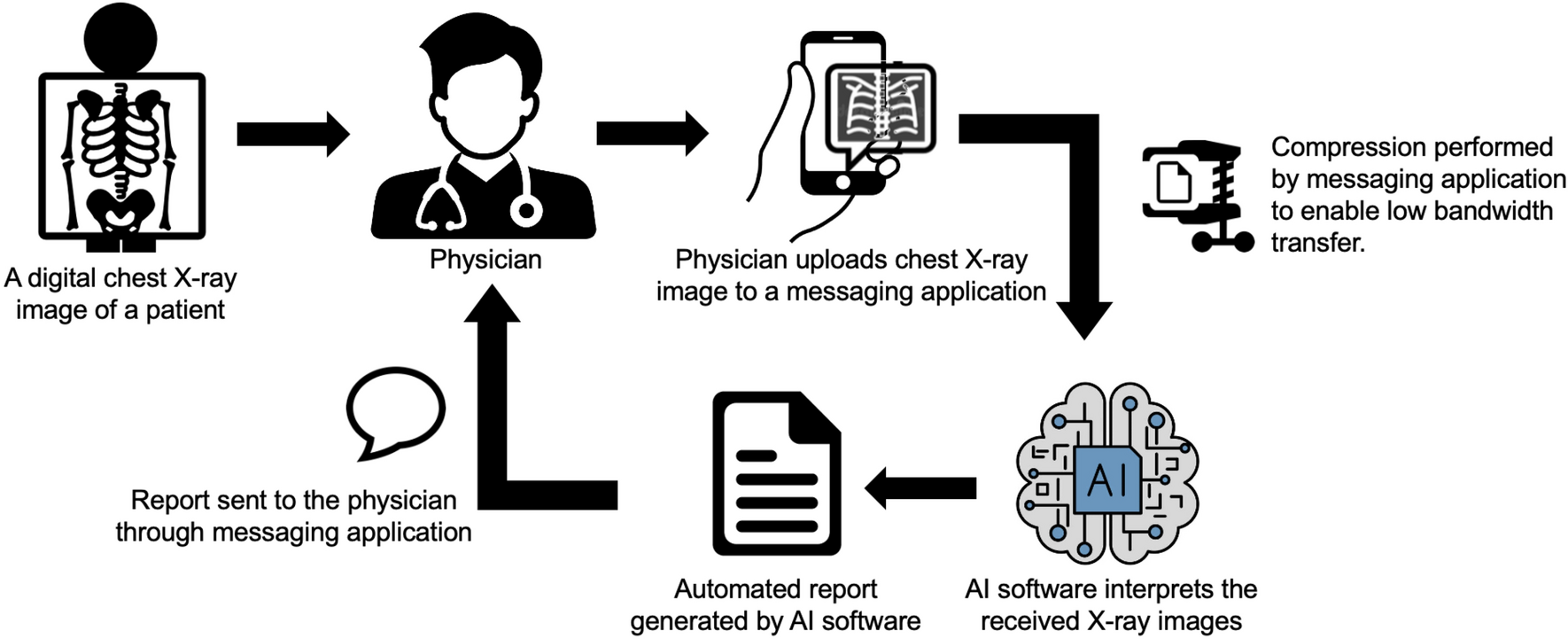
Audit work for X-ray reporting involves a systematic review and evaluation of radiology reports to assess the quality, accuracy, and completeness of interpretations provided by radiologists. The primary goal of X-ray reporting audits is to ensure that radiology reports meet established standards of practice, comply with regulatory requirements, and contribute to optimal patient care. Here’s how audit work for X-ray reporting is typically conducted:
- Establish Audit Criteria: Define audit criteria and performance indicators based on professional guidelines, best practices, and institutional policies. Audit criteria may include accuracy of interpretations, completeness of reports, adherence to standardized terminology, appropriateness of recommendations, and timeliness of reporting.
- Selection of Sample Cases: Select a representative sample of X-ray reports for audit review. Sample selection may be randomized or targeted based on specific criteria such as modality type, anatomical region, clinical indication, and complexity of findings. Ensure that the sample size is sufficient to yield meaningful insights and statistical analysis.
- Review Process: Conduct a comprehensive review of selected X-ray reports by qualified reviewers, which may include radiologists, radiology residents, clinical experts, or quality assurance specialists. Reviewers assess each report against predefined audit criteria, document findings, and identify areas for improvement or corrective action.
- Evaluation of Accuracy: Evaluate the accuracy and diagnostic validity of radiology interpretations by comparing reported findings with corresponding imaging findings documented in the X-ray images. Assess the concordance between radiology reports and clinical outcomes to determine the diagnostic efficacy and reliability of interpretations.
- Assessment of Completeness: Evaluate the completeness and comprehensiveness of radiology reports by assessing the inclusion of essential components such as patient demographics, clinical history, imaging technique, findings, impressions, differential diagnoses, recommendations, and follow-up instructions.
- Documentation of Audit Findings: Document audit findings, including strengths, deficiencies, discrepancies, and opportunities for improvement identified during the review process. Summarize key observations, trends, and patterns observed across the sample cases to facilitate data analysis and reporting.
- Analysis and Reporting: Analyze audit data to identify trends, root causes of discrepancies, and areas of non-compliance with audit criteria. Prepare audit reports summarizing findings, recommendations, and action plans for quality improvement initiatives. Share audit results with relevant stakeholders, including radiologists, referring clinicians, departmental leaders, and quality assurance committees.
- Quality Improvement Initiatives: Implement targeted interventions and quality improvement initiatives based on audit findings to address identified deficiencies and enhance the overall quality and effectiveness of X-ray reporting practices. Develop educational programs, training sessions, feedback mechanisms, and workflow optimizations to support continuous learning and performance enhancement.
- Monitoring and Follow-up: Monitor the effectiveness of quality improvement initiatives and track progress towards achieving audit objectives and performance goals. Conduct periodic follow-up audits to assess ongoing compliance, identify emerging issues, and measure the impact of quality improvement efforts over time.
By conducting systematic audit work for X-ray reporting, healthcare organizations can promote accountability, transparency, and excellence in radiology practice, ultimately leading to improved patient outcomes, enhanced diagnostic accuracy, and enhanced patient safety.
